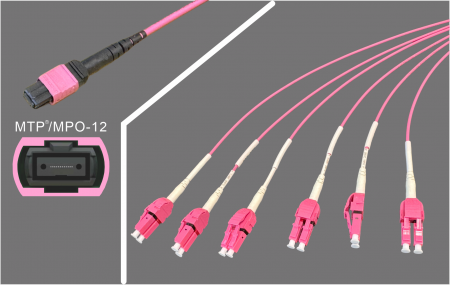
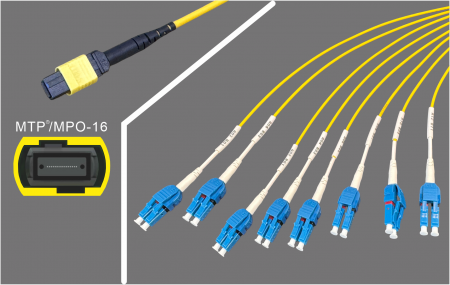
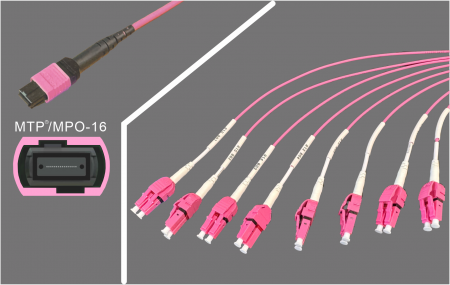
MPO to LC Breakout
MPO → LC Breakout
MPO to LC Breakout
Recent advancements in breakout connectivity are becoming increasingly important as higher-speed ports appear on switches, routers, and other networking equipment. Breakouts allow these high-speed ports to interface with lower-speed ports, providing flexibility in how bandwidth is allocated.
MPO trunks are designed for high-density fiber cabling, carrying 12, 16, or even more fibers in a single connector. However, most transceivers on servers and switches still use LC duplex ports rather than MPO. A breakout cable converts the high-density MPO trunk into multiple LC duplex connections, making the fibers directly usable at the device level.
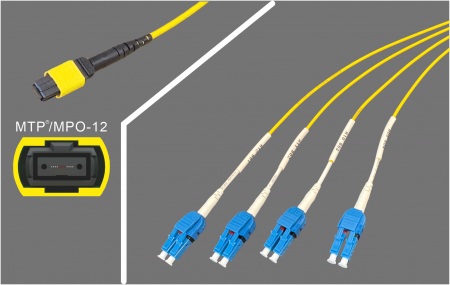
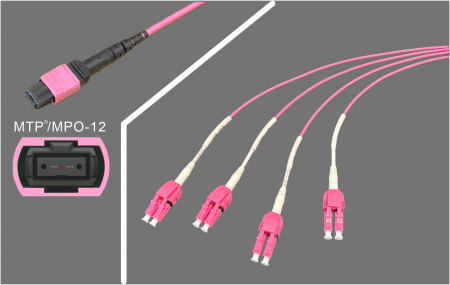
The most common conversion is MPO to four LC duplex ports. A 400G-DR4 transceiver uses 4 transmit and 4 receive lanes (8 fibers total). Alternatively, an MPO-12 can be broken out into 4 BiDi connections, with each link carrying both transmit and receive signals over a single fiber by using two different wavelengths.
MPO-12(4-lane) to 4×LC Duplex:
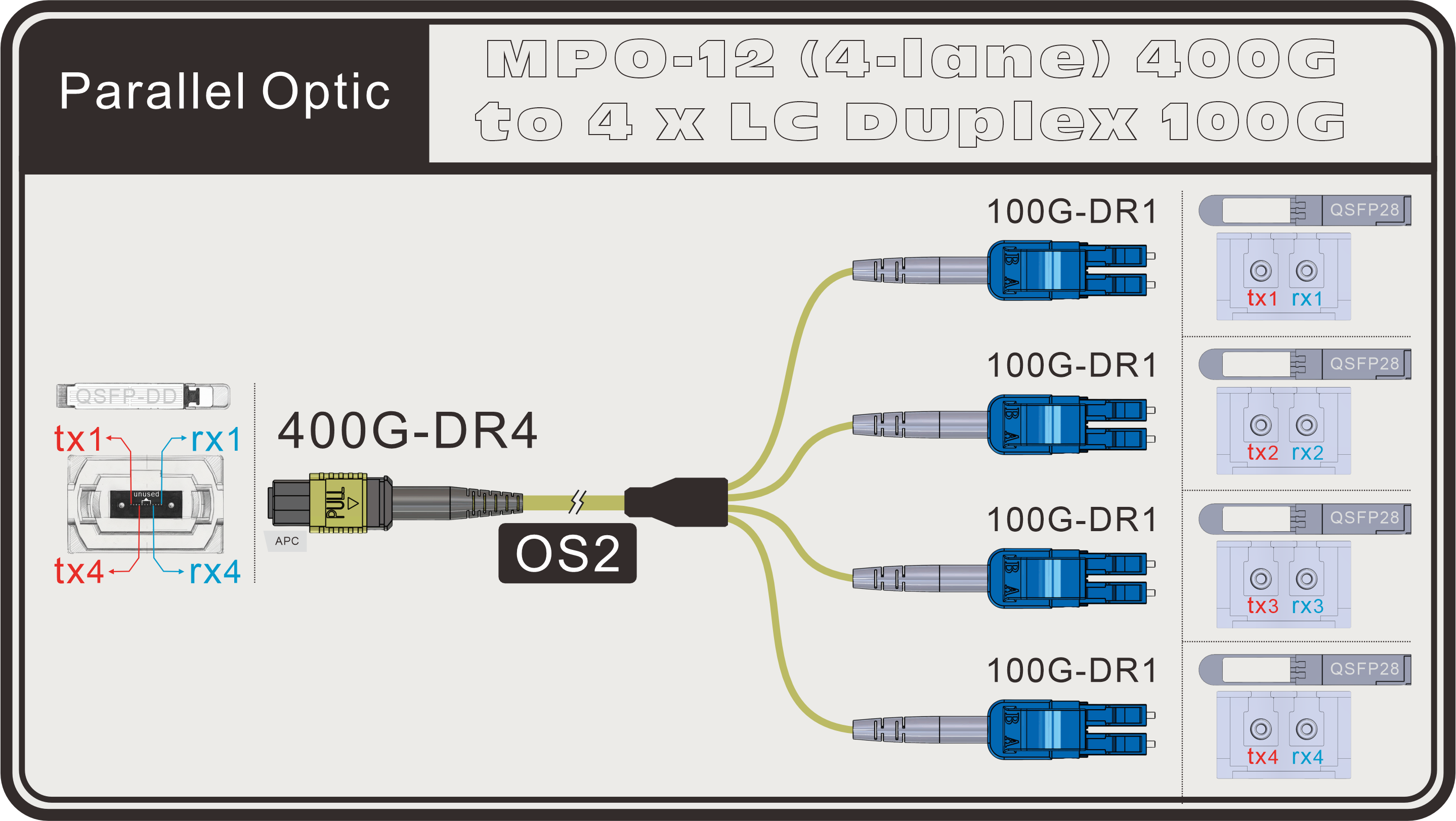
- With an MPO-12 trunk, these lanes can be broken out into four 100G LC duplex connections, each feeding an individual 100G server. This flexibility helps maximize port utilization and simplifies network design.
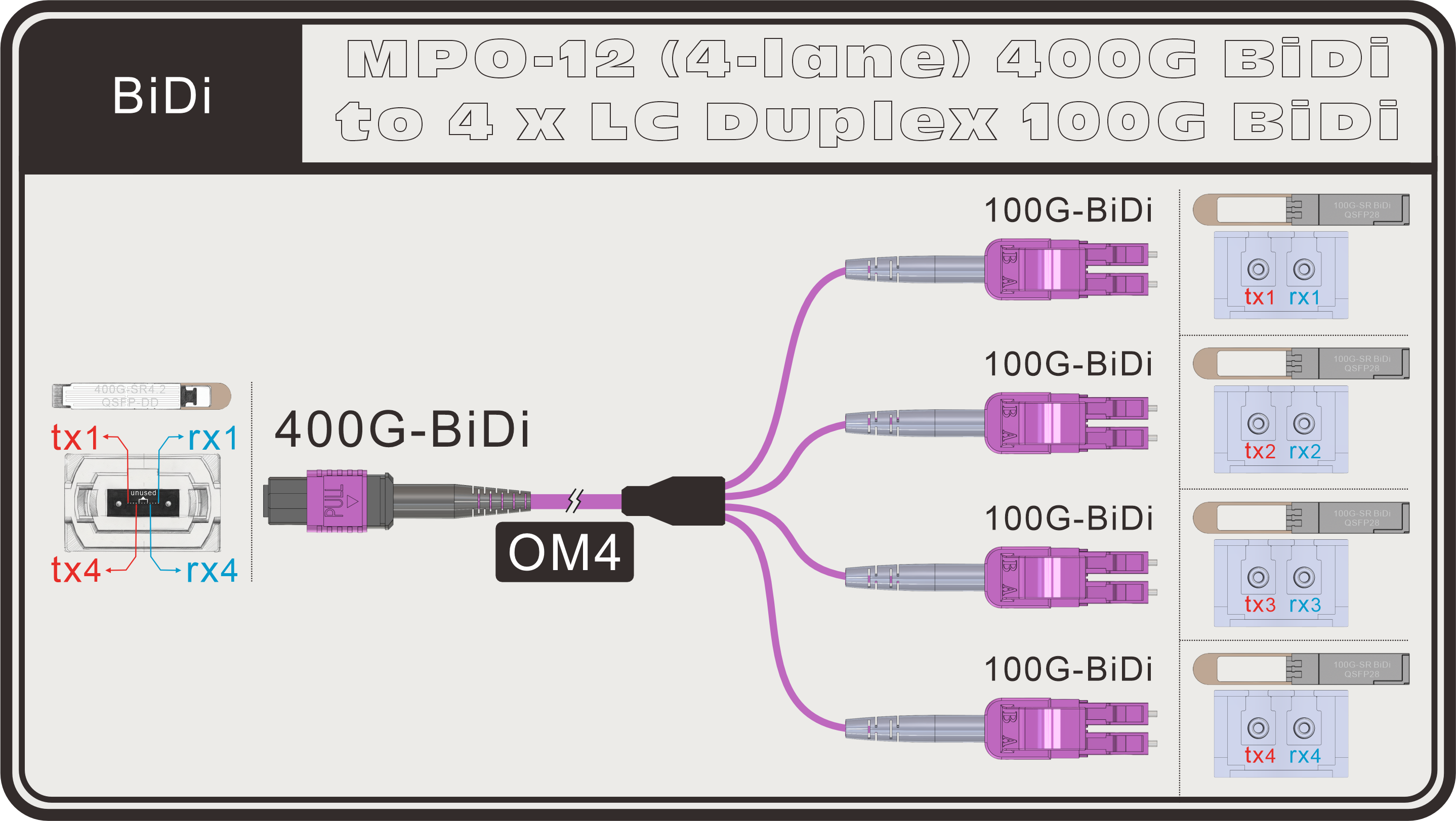
- BiDi – each of the four links operates over a single fiber, using two wavelengths (one for Tx and one for Rx) to carry data.
By combining high-density MPO trunks with breakout cables, networks can bridge the gap between backbone cabling and device-ready LC connections. This approach supports parallel optics while providing flexible scaling for both current and future data center needs.
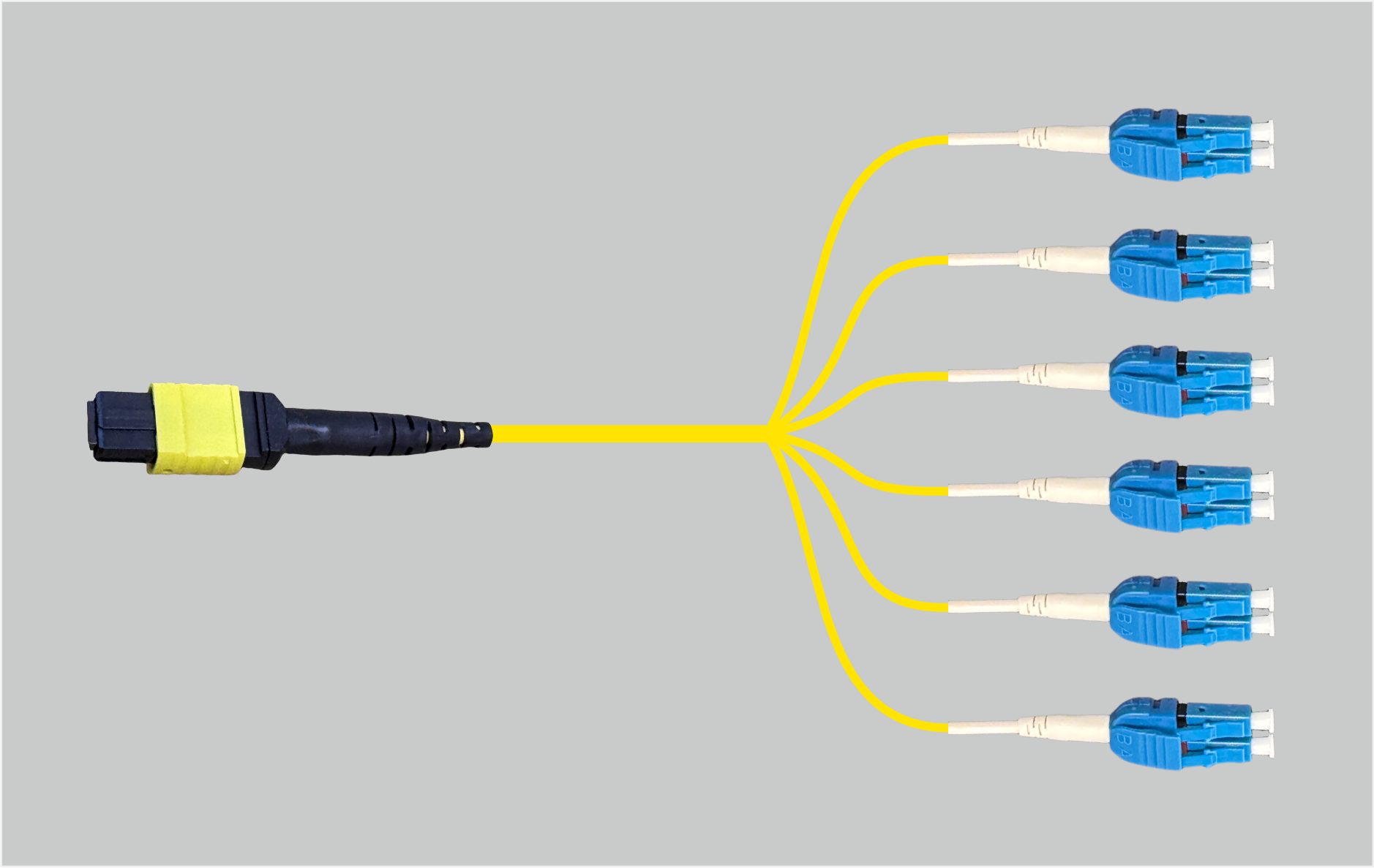
Alternatively, all 12 fibers can be used, with 6 lanes broken out into six ready-to-use LC duplex connections.
MPO-12 to 6×LC Duplex:
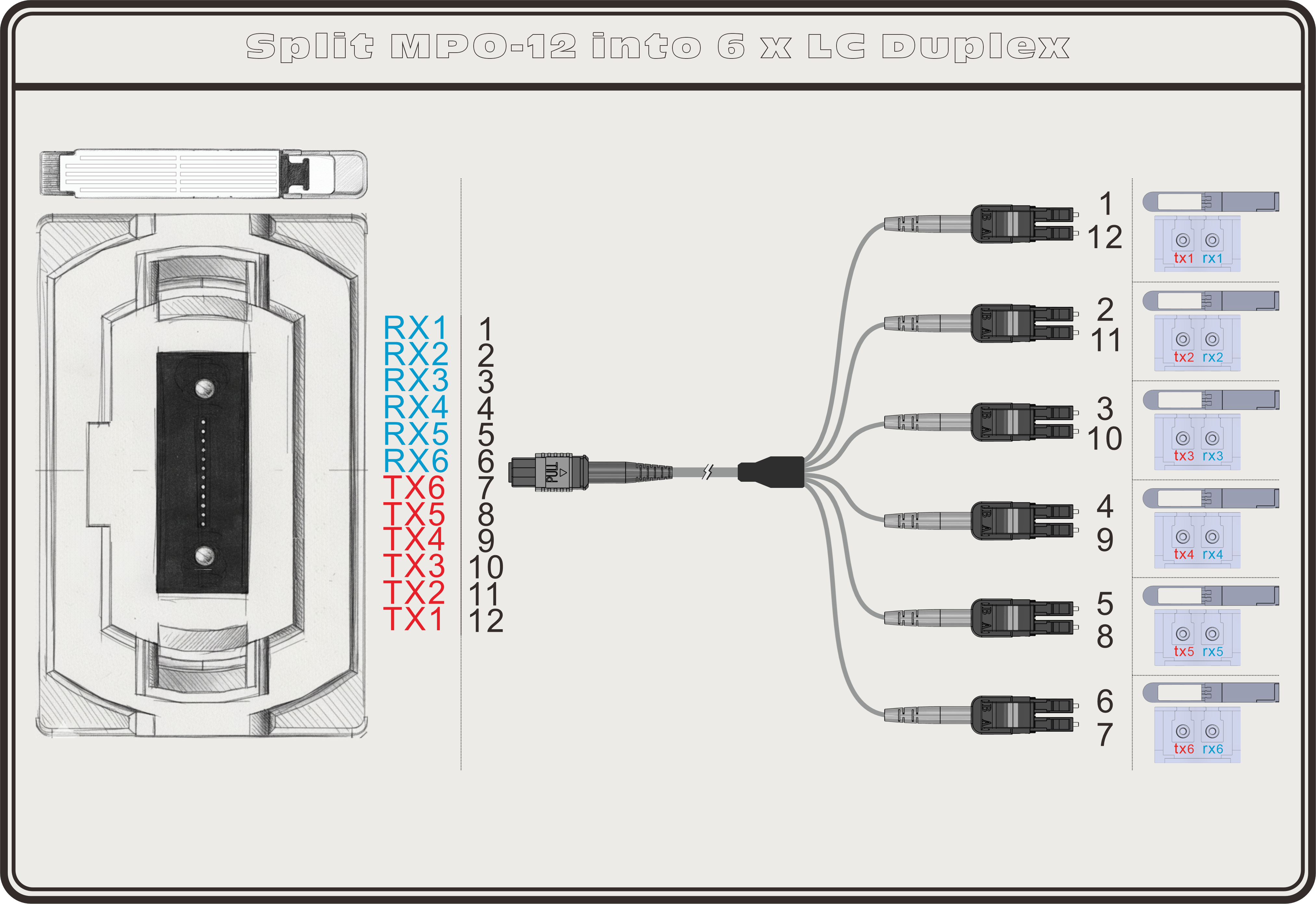
- The wiring is arranged so that MPO transmit lanes map directly to LC receive lanes (and vice versa), eliminating the need for an additional polarity flip.
Breakouts also improve cable management. They reduce clutter in racks, maintain better airflow, and make future upgrades easier. When it’s time to refresh server connections, you only need to replace the breakout cable, leaving the main MPO trunks untouched.
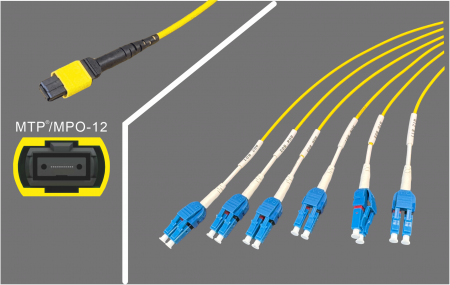
Another approach is to utilize all 16 fibers (8 lanes) and break them into eight LC duplex connections.
MPO-16 to 8×LC Duplex:
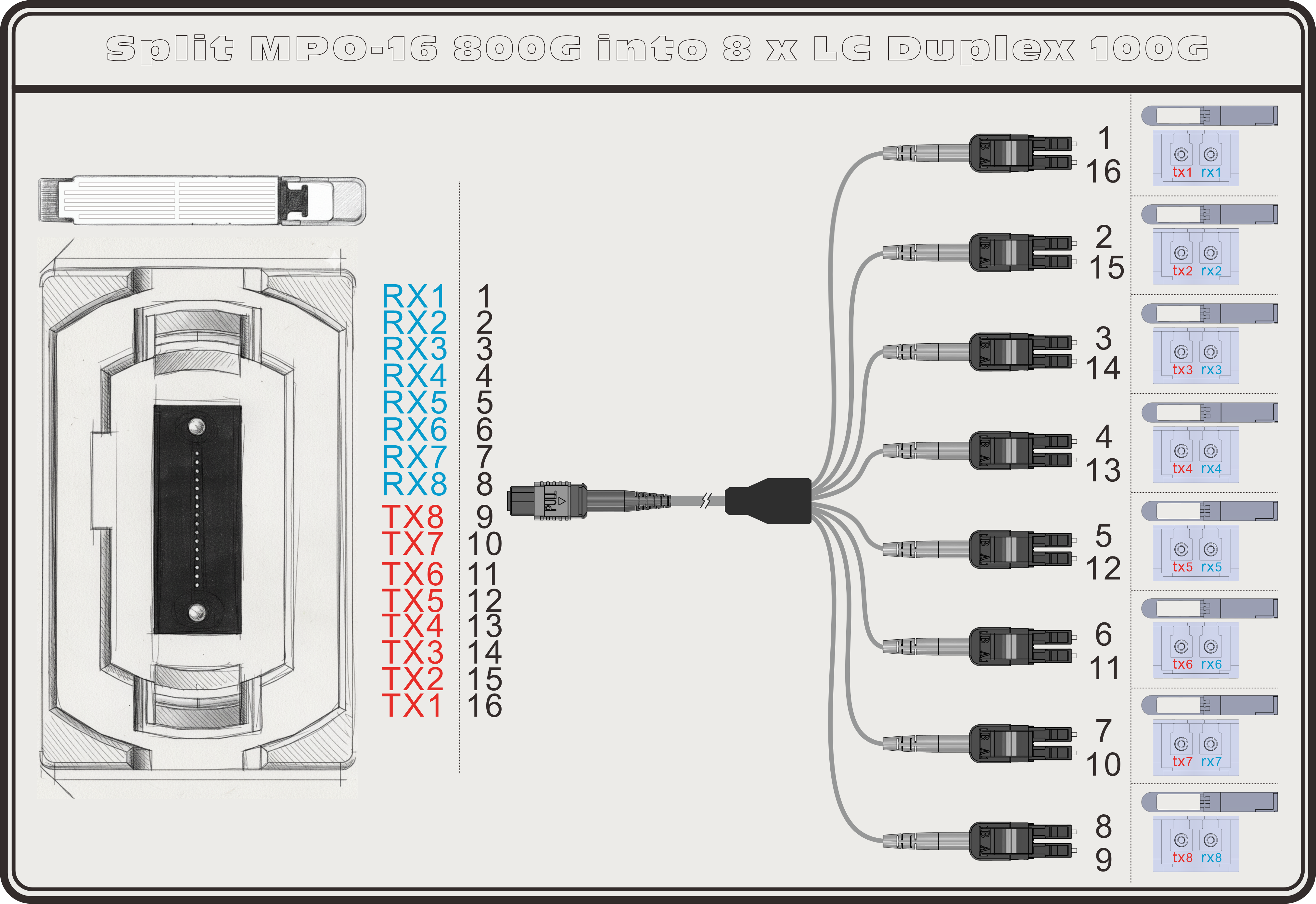
- This allows a full 800G-DR link to be broken into 8×100G-DR connections over OS2 fiber, ideal for intra–data center conversion. The wiring again aligns MPO Tx to LC Rx for straightforward deployment.
We offer MPO and MTP connectors with reversed wiring as the default, since this is the most common setup in data centers. Custom wiring is also available — simply specify the pinouts for both MPO and LC terminations, and we can have it made!
Our product groups:
- MPO-12 → 4 × LC Duplex (SMF)
- MPO-12 → 4 × LC Duplex (MMF)
- MPO-12 → 6 × LC Duplex (SMF)
- MPO-12 → 6 × LC Duplex (MMF)
- MPO-16 → 8 × LC Duplex (SMF)
- MPO-16 → 8 × LC Duplex (MMF)
Select your group, provide the options step by step, and we’ll deliver exactly what you need.